In high-end manufacturing fields such as semiconductors and precision optics, granite slicing bases have become key components of core equipment due to their excellent stability and wear resistance. However, the market is flooded with counterfeit and shoddy products that pass off marble, artificial stone and even dyed stone, which not only leads to a decline in equipment accuracy, but also may cause huge losses. This article provides a scientific identification guide from three dimensions: material properties, testing methods, and certification systems, to help you avoid consumer traps.
I. Material Characteristics: Basic Knowledge for Identifying Camouflage
1. Hard indicators of density and hardness
True granite: Its density is typically between 2600 and 3100kg/m³ (high-quality black granite such as ZHHIMG® products can reach over 3000kg/m³), with a Mohs hardness of 6 to 7. When a coin is scratched across its surface, there is no trace left.
Counterfeit product: The density of marble is approximately 2500-2700kg/m³, and its hardness is only 3-5 grades. A light scratch on a coin leaves a mark. The density of artificial stone fluctuates greatly and it makes a dull sound when struck (while real granite makes a clear sound).
2. Microscopic differences in structure and texture
Natural granite: It is composed of mineral particles such as quartz and feldspar that are closely interwoven. Its texture features irregular spots or stripes, and its cross-section is rough with a distinct granular feel.
Dyed stone: The surface texture is dull. It may fade when wiped with alcohol, and the color of the cross-section is significantly different from that of the surface. The texture of marble is mostly continuous stripes and contains calcium carbonate crystals (which will bubble when dilute hydrochloric acid is dropped on them).
Ii. Scientific Testing: Exposing Lies with Data
1. Basic performance test
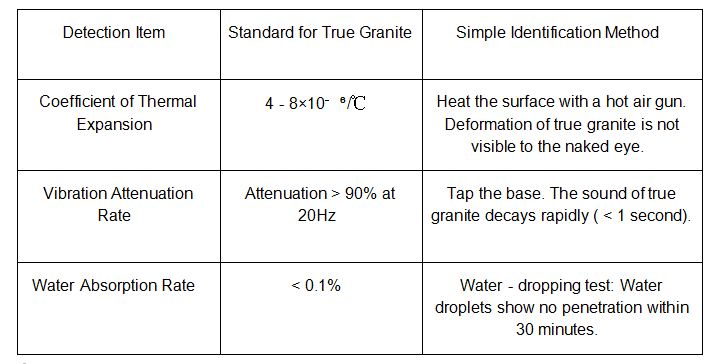
2. Professional instrument identification
Ultrasonic flaw detection: Genuine granite shows no obvious defect echoes inside, while fake materials may have cracks or hollow reflections.
X-ray diffraction analysis: It can precisely determine the mineral composition (granite mainly contains quartz and feldspar, while marble is mainly composed of calcite).
Iii. Certification System: An authoritative certificate for Risk Avoidance
List of must-check documents
Proof of ore vein traceability: For genuine granite, specific information about the quarry should be provided (such as Shandong Jinan Black, Indian Black).
Third-party test report: Including key data such as density, hardness, and coefficient of thermal expansion (issued by a CNAS or ISO 17025 certified laboratory);
ISO Quality Certification: Regular manufacturers need to pass the ISO 9001 quality management system certification, and high-end products need to be accompanied by the ISO 14001 environmental certification.
2. Be vigilant against the traps of false advertising
Products claiming to be "all-purpose stone" or "supernatural hardness" are mostly gimmicks.
Bases without specific technical parameters (such as flatness and straightness) should be purchased with caution.
Products whose prices are more than 30% lower than the market average are likely to be counterfeit or substandard.
Post time: Jun-12-2025

